Graphene is a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like pattern. Graphene is considered to be the world's thinnest, strongest and most conductive material - of both electricity and heat. All of these properties are exciting researchers and businesses around the world - as graphene has the potential to revolutionize entire industries - in the fields of electricity, conductivity, energy generation, batteries, sensors and more.
Mechanical strength
Graphene is the world's strongest material, and can be used to enhance the strength of other materials. Dozens of researchers have demonstrated that adding even a trace amount of graphene to plastics, metals or other materials can make these materials much stronger - or lighter (as you can use a smaller amount of material to achieve the same strength).

Such graphene-enhanced composite materials can find uses in aerospace, building materials, mobile devices, and many other applications.
Thermal applications
Graphene is the most heat conductive found to date. As graphene is also strong and light, it means that it is a great material for making heat-spreading solutions, such as heat sinks or heat dissipation films. This could be useful in both microelectronics (for example to make LED lighting more efficient and longer lasting) and also in larger applications - for example thermal foils for mobile devices. Huawei's latest smartphones, for example, have adopted graphene-based thermal films.

Energy storage
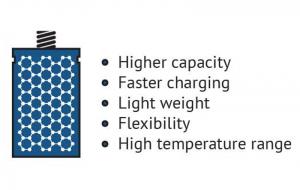
Since graphene is the world's thinnest material, it also extremely high surface-area to volume ratio. This makes graphene a very promising material for use in batteries and supercapacitors. Graphene may enable batteries and supercapacitors (and even fuel-cells) that can store more energy - and charge faster, too.
 The advantages of graphene batteries
The advantages of graphene batteries
Coatings ,sensors, electronics and more
Graphene has a lot of promise for additional applications: anti-corrosion coatings and paints, efficient and precise sensors, faster and efficient electronics, flexible displays, efficient solar panels, faster DNA sequencing, drug delivery, and more.
Graphene is such a great and basic building block that it seems that any industry can benefit from this new material. Time will tell where graphene will indeed make an impact - or whether other new materials will be more suitable.
The latest Graphene Application news:
Researchers design a butterfly-inspired multisensory neuromorphic platform for integration of visual and chemical cues
It is a known fact that animals require the integration of cues collected from multiple sensory organs to enhance the overall perceptual experience and thereby facilitate better decision-making in most aspects of life. However, despite the importance of multisensory integration in animals, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and neuromorphic computing has primarily focused on processing unisensory information. This lack of emphasis on multisensory integration can be attributed to the absence of a miniaturized hardware platform capable of co-locating multiple sensing modalities and enabling in-sensor and near-sensor processing.
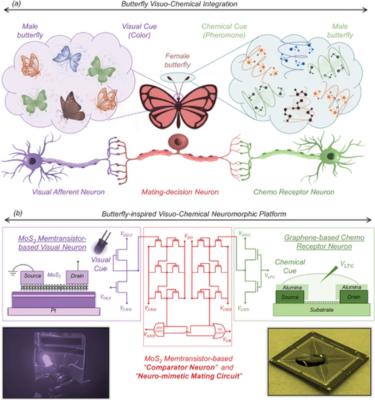
a) A simplified abstraction of visual and chemical stimuli from male butterflies and visuo-chemical integration pathway in female butterflies. b) Butterfly-inspired neuromorphic hardware comprising of monolayer MoS2 memtransistor-based visual afferent neuron, graphene-based chemoreceptor neuron, and MoS2 memtransistor-based neuro-mimetic mating circuits. Image credit: Advanced Materials
In their recent study, researchers at Penn State University addressed this limitation by utilizing the chemo-sensing properties of graphene and the photo-sensing capability of monolayer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) to create a multisensory platform for visuochemical integration.
Graphene-Info publishes a new edition of its Graphene Supercapacitors Market Report
Today we published a new edition of our Graphene Supercapacitors Market Report, with all the latest information. The supercapacitor market and industry is facing high demand and graphene is a pivotal material for this application. This new update includes many updates from various projects and research activities
Reading this report, you'll learn all about:
- The advantages of using graphene in supercapacitors
- Various types of graphene materials
- Market insights and forecasts
- What's on the market today
The report package also provides:
- A list of all graphene companies involved with supercapacitors
- Prominent research activity in this field
- Free updates for a year
This Graphene Supercapacitors market report provides a great introduction to graphene materials used in the supercapacitor market, and covers everything you need to know about graphene in this niche. This is a great guide for anyone involved with the supercapacitor market, nanomaterials, electric vehicles and mobile devices.
Sparc and DIT to test graphene coatings on steel infrastructure
Sparc Technologies and the South Australian Department for Infrastructure and Transport (DIT) have announced they will be trialing the Company’s ecosparc graphene enhanced coatings on steel infrastructure such as bridges and jetties in Australia. The parties have signed a trial agreement under which Sparc and the DIT will conduct collaborative field trials at the West Beach Bridge in Adelaide and the Streaky Bay Jetty on the Eyre Peninsula.
The DIT has approximately $45 billion in assets with the supply of the ecosparc enhanced expected imminently.
Pacific Basin announces the use of graphene-based propeller coating
Hong Kong-based Pacific Basin, one of the world's leading owners and operators of dry bulk ships, has decided to apply a graphene-based propeller coating, XGIT-PROP, across its entire fleet.
The biocide-free hard foul release coating, developed by Canadian company GIT Coatings, has demonstrated the potential to enhance vessel performance by up to 4%, the two companies stated in a release citing data from earlier tests carried out by Stolt Tankers.
2D Fab joins consortium for next-gen bio-adhesives
2D Fab has become a partner of the new consortium BioGlue-Centre, a collaborative initiative to make Sweden a front runner in the development of bio-based adhesives.
BioGlue-Centre is a collaborative effort between three universities and 12 companies, including 2D Fab. With a shared focus on advancing adhesive technologies, the Centre addresses the critical need for sustainability by accelerating the development of bio-based alternatives within the adhesive industry.
Researchers create graphene-integrated bioelectronic mesh for tracking multimodal excitation-contraction dynamics in cardiac microtissues
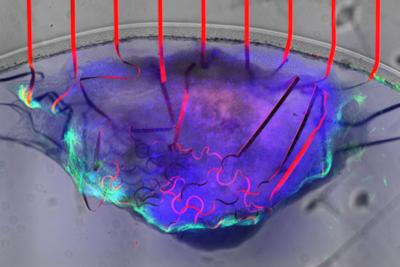
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have successfully built a tissue-like bioelectronic mesh system integrated with an array of graphene sensors that can simultaneously measure both the electrical signal and the physical movement of cells in lab-grown human cardiac tissue.
A bioelectronic mesh, studded with graphene sensors (red), can measure the electrical signal and movement of cardiac tissue (purple and green) at the same time. Image credit: UMass Amherst
The tissue-like mesh can grow along with the cardiac cells, allowing researchers to observe how the heart’s mechanical and electrical functions change during the developmental process. The new device can be extremely useful for those studying cardiac disease as well as those studying the potentially toxic side-effects of many common drug therapies.
First Graphene announces low-cost, high-performing graphene-based electrocatalysts
First Graphene has developed a low-cost, high-performing graphene-based electrocatalyst that targets the rapidly growing production of ‘green hydrogen’ by water electrolysis. Electrocatalysts are used to produce ‘green hydrogen’, but currently require high-cost rare metals such as iridium and ruthenium which can drive up operating costs. First Graphene’s solution uses its PureGRAPH® technology to produce higher-performing, affordable electrocatalysts.
First Graphene has completed a 12-month project in the United Kingdom to develop low-cost, high-performing electrocatalysts for hydrogen production.
Levidian unveils graphene-enhanced prototype truck tire
Levidian has unveiled its first prototype truck tire, combining graphene with carbon black in a new tread formulation. Launched this week at the Tire Technology Expo in Hannover, the graphene-enhanced natural rubber and butadiene rubber tire tread compound, typically used in commercial vehicle tires, has been shown to deliver significant improvements in the mechanical and dynamic properties of the tire.
Independent testing by the Tun Abdul Razak Research Centre (TARRC) has reportedly shown that the addition of Levidian’s 'net zero graphene' can deliver a reduction in rolling resistance of around 23%. Initial results have also indicated potential for reduced compound density that could allow for lighter tires overall. It was said that overall, this could deliver substantial improvements in fuel efficiency of 3-4%.
Researchers develop approach for creating tight arrangement of bilayer alkali metals between graphene layers for improved batteries
Researchers at AIST, Osaka University, Tokyo Polytechnic University, Kyushu University, and National Tsing Hua University, have developed a technique to insert alkali metals (AMs) into the interlayers of graphene. They them used low-voltage scanning transmission electron microscopy (LV-STEM) to visualize the atomic structure of the intercalated AMs (potassium, rubidium, and cesium) in the bilayer graphene (BLG). The team's findings revealed that the intercalated AMs adopt bilayer structures with hcp stacking, and specifically a C6M2C6 composition.
The performance of rechargeable batteries is a key factor influencing the driving distance of electric vehicles and the usage time of smartphones. Improving the performance of these electronic devices is possible if rechargeable batteries can accumulate greater electrical capacities. Graphite, the electrode material used in batteries, is composed of multilayers of graphene, with alkali metals placed between the layers to facilitate the flow of electrons during charging and discharging. Achieving a high density of alkali metals storage between graphene layers could increase the electric capacity.
Researchers develop deformable graphene-based liquid metal micro-supercapacitors
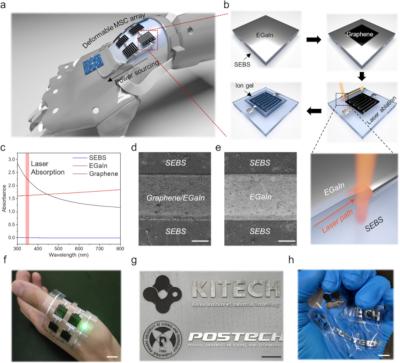
Researchers from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Korea Institute of Industrial Technology and Konkuk University have fabricated highly deformable graphene-based micro supercapacitors (MSCs) using liquid metal current collectors on an elastic polymer substrate.
a Illustration of an integrated system comprising soft-electronics and deformable energy storage component. b The fabrication process of EGaIn-based MSC. c UV-vis spectra of SEBS, EGaIn, and graphene. FE-SEM images of laser ablated d Graphene/EGaIn and e EGaIn (Scale bar = 200 µm). Photographs of f institute logos, g deformed logos, and h an LED connected to the MSC circuit (Scale bar = 1 cm). (Image from npj Flexible Electronics)
The team used eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn), a liquid metal alloy, as the current collector since a deformable current collector is needed in order to create a deformable MSC. Commonly used current collectors made of brittle materials like gold (Au) are not suitable in this case, so the team turned to 'liquid metal' that inherently possesses the properties of a liquid and metallic conductivity.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page