Graphene applications: what is graphene used for?
Graphene is a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like pattern. Graphene is considered to be the world's thinnest, strongest and most conductive material - of both electricity and heat. All of these properties are exciting researchers and businesses around the world - as graphene has the potential to revolutionize entire industries - in the fields of electricity, conductivity, energy generation, batteries, sensors and more.
Mechanical strength
Graphene is the world's strongest material, and can be used to enhance the strength of other materials. Dozens of researchers have demonstrated that adding even a trace amount of graphene to plastics, metals or other materials can make these materials much stronger - or lighter (as you can use a smaller amount of material to achieve the same strength).

Such graphene-enhanced composite materials can find uses in aerospace, building materials, mobile devices, and many other applications.
Thermal applications
Graphene is the most heat conductive found to date. As graphene is also strong and light, it means that it is a great material for making heat-spreading solutions, such as heat sinks or heat dissipation films. This could be useful in both microelectronics (for example to make LED lighting more efficient and longer lasting) and also in larger applications - for example thermal foils for mobile devices. Huawei's latest smartphones, for example, have adopted graphene-based thermal films.

Energy storage
Since graphene is the world's thinnest material, it also extremely high surface-area to volume ratio. This makes graphene a very promising material for use in batteries and supercapacitors. Graphene may enable batteries and supercapacitors (and even fuel-cells) that can store more energy - and charge faster, too.
 The advantages of graphene batteries
The advantages of graphene batteries
Coatings ,sensors, electronics and more
Graphene has a lot of promise for additional applications: anti-corrosion coatings and paints, efficient and precise sensors, faster and efficient electronics, flexible displays, efficient solar panels, faster DNA sequencing, drug delivery, and more.
Graphene is such a great and basic building block that it seems that any industry can benefit from this new material. Time will tell where graphene will indeed make an impact - or whether other new materials will be more suitable.
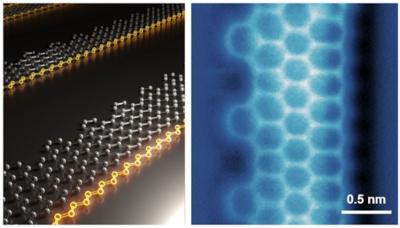
Unique GNRs could advance quantum technologies
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS), working with teams from University of California, Kyoto University and others, have reported a breakthrough in the development of next-generation graphene-based quantum materials, opening new horizons for advancements in quantum electronics.
An atomic model of the Janus graphene nanoribbons (left) and its atomic force microscopic image (right). Image credit: NUS
The innovation involves a novel type of graphene nanoribbon (GNR) named Janus GNR (JGNR). The material has a unique zigzag edge, with a special ferromagnetic edge state located on one of the edges. This unique design enables the realization of one-dimensional ferromagnetic spin chain, which could have important applications in quantum electronics and quantum computing.
POSTECH and University of Technology Sydney develop quantum LED using graphene
A collaborative effort involving POSTECH and the University of Technology Sydney has yielded an advancement in light source technology. The team used graphene to develop a quantum light emitting diode (Quantum LED) that can precisely emit light using a single atom. This innovative technology generates light by injecting charges into a luminescent material composed of a single atom.
The research team implemented this advanced light source technology using hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), a material known for its ability to stably confine electrons in various atomic defects. Unlike traditional quantum dots, which are composed of hundreds to thousands of atoms, the quantum LED developed by the team exhibits excellent quantum light source characteristics even at room temperature. This breakthrough addresses a significant challenge in the field, as hBN's wide bandgap has historically made it difficult to inject charges electrically, thus hindering the development of LED devices. To overcome this obstacle, the researchers designed a "graphene-hBN-graphene" van der Waals tunneling structure.
LG unveils “xboom by will.i.am” product line, that includes graphene-enhanced earbuds, at CES
LG Electronics (LG) has unveiled its new “xboom by will.i.am” audio product line of Bluetooth speakers and earbuds at CES 2025, created in partnership with musician and tech entrepreneur, will.i.am.
The xboom Buds employ lightweight graphene drivers, which are key to delivering pure, well-balanced sound with rich bass. Graphene is said to improve durability while supporting LG’s Active Noise Canceling technology, providing a more immersive listening experience. Featuring LE Audio Auracast, the Buds enable users to listen to open audio streams in public and permit multiple device connections so that several users can simultaneously enjoy the same audio. Designed for comfort and stability, the ergonomic ear tips adapt to various ear shapes, while the unique ear hook design provides a snug and stable fit on the go. It offers up to 30 hours of listening time with the support of its charging case, as well as IPX4 water resistance that protects against splashing water.
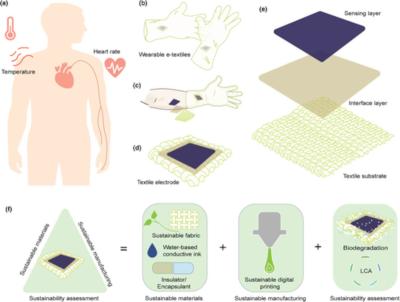
Graphene-based sustainable E-textiles for early detection of diseases
A research team, led by the University of Southampton and UWE Bristol, has developed graphene-based wearable electronic textiles (e-textiles) that are sustainable and biodegradable. In their new study, the team (which also involved the universities of Exeter, Cambridge, Leeds and Bath), describes and tests a new sustainable approach for fully inkjet-printed, eco-friendly e-textiles named 'Smart, Wearable, and Eco-friendly Electronic Textiles', or 'SWEET'.
a) Schematic of two important vital signs: skin surface temperature and heart rate of the human body. b) Schematic of wearable e-textiles as gloves. c) Schematic of the position of wearable textile electrode on human skin surface contact. d) Schematic of the textile electrode. e) Schematic of the textile electrodes' composition. f) Schematic of sustainable design approach for wearable e-textiles, including sustainable materials, sustainable manufacturing, and sustainability assessment. Image from: Energy and Environmental Materials
E-textiles are usually embedded with electrical components, such as sensors, batteries or lights. They might be used in fashion, for performance sportwear, or for medical purposes as garments that monitor people's vital signs. Such textiles need to be durable, safe to wear and comfortable, but also, in an industry which is increasingly concerned with clothing waste, they need to be easy on the environment when no longer required.
2D Fab announces the installation of concrete center railings reinforced with nanotechnology in Sundsvall
2D Fab has marked a milestone in its journey toward more sustainable concrete for road applications, with the installation of concrete center railings reinforced with nanotechnology (presumably graphene, as the company is a longtime graphene producer) in Sundsvall.
It reported that earlier this week, four out of eight of the old concrete center railings along Skolhusallén in Sundsvall were replaced with new railings reinforced with nanotechnology, paving the way for more sustainable infrastructure. These new center railings bring both improved frost resistance, and greater durability.
Versarien launches new graphene biosensor chip technology
Versarien has launched a new biosensor chip utilizing novel graphene barristor sensor platform technology. These graphene barristor devices, developed in South Korea by A Barristor Company (ABC), will utilize chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene, that is produced under a Versarien license. Versarien has signed a distribution agreement with ABC to distribute the products in the UK and Europe.
A barristor (triode device) is a new type of graphene‐based transistor with a Schottky barrier between graphene and silicon. The current modulation is amplified more than 10,000 times compared to graphene field‐effect transistors (GFET), enabling the barristor transistors to overcome many GFET limitations.
Bio Graphene Solutions announces successful graphene-enhanced concrete pilot project with EllisDon Corporation in coordination with Tomlinson Ready Mix
Bio Graphene Solutions (BGS) has announced that it has completed a pilot commercial concrete pour with EllisDon Corporation, a global construction services and technology company, and Tomlinson Ready Mix, one of Ottawa’s largest concrete providers and part of the Tomlinson Group of Companies.

The Company’s proprietary graphene-enhanced admixture was integrated into the operational flow of a Tomlinson Ready Mix 32MPa-C-2 sidewalk concrete pour at an active construction project managed by EllisDon’s Ottawa team. The biographene-enhanced concrete mix utilized 10% less cement than the control mix design without sacrificing the fresh properties of the concrete. This pilot testing is a critical milestone in demonstrating the in-situ performance of the biographene-enhanced mix, validating lab trials which have shown that the concrete achieves the 28-day targeted strength of 32MPa by 7 days.
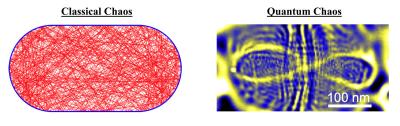
Graphene experiment proves patterns in chaos in quantum realm
Researchers from the University of California, Harvard University, University of Manchester, UC Santa Cruz and the National Institute for Materials Science in Tsukuba, Japan have conducted an experiment that confirms a 40 year old theory that electrons confined in quantum space would move along common paths rather than producing a chaotic array of trajectories.
Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like properties and behave in ways that are often counterintuitive, and under certain conditions, their waves can interfere with each other in a way that concentrates their movement into certain patterns. Physicists call these common paths “unique closed orbits.”
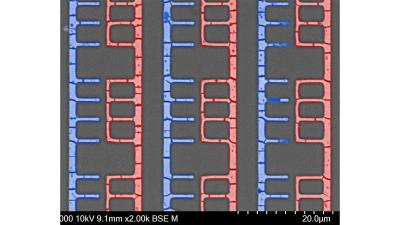
Researchers use graphene in novel technique for self-assembling electronics
Researchers from North Carolina State University and Iowa State University have demonstrated a new technique for self-assembling electronic devices. The proof-of-concept work was used to create diodes and transistors, and could pave the way for self-assembling more complex electronic devices without relying on existing computer chip manufacturing techniques.
D-Met fabricated patterns produce components for potential use in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Image credit: Julia Chang and NCSU.
“Existing chip manufacturing techniques involve many steps and rely on extremely complex technologies, making the process costly and time consuming,” says Martin Thuo, corresponding author of a paper on the work and a professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University. “Our self-assembling approach is significantly faster and less expensive. We’ve also demonstrated that we can use the process to tune the bandgap for semiconductor materials and to make the materials responsive to light – meaning this technique can be used to create optoelectronic devices. What’s more, current manufacturing techniques have low yield, meaning they produce a relatively large number of faulty chips that can’t be used. Our approach is high yield – meaning you get more consistent production of arrays and less waste.”
Graphene transistors could enable ultrasensitive detection of infections
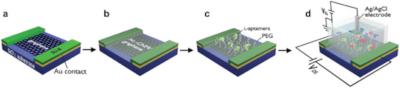
Researchers from Friedrich Schiller University Jena, CNM Technologies, NOXXON Pharma, APTARION Biotech and Radboud University Medical Center have developed graphene field effect transistor (GFET) sensors based on van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures of single-layer graphene layered with a molecular ≈1 nm thick carbon nanomembrane (CNM).
1 / 1Schematic illustration of the fabrication steps of the l-AP/PEG-CNM GFET sensors. Credit: Advanced Materials
The CNM acts as an ultrathin molecular interposer between the graphene channel and the analyte and allows bio-functionalization without impairing the graphene properties including its charge carrier mobility.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page