Graphene and water treatment: introduction and market status - Page 2
Evove secures over $6.7 million to advance its graphene-based for its water filtration technology
UK-based Evove, developer of a graphene-based water filtration technology designed to tackle water shortage, has announced that it has secured £5.7 million (around USD$6,750,000) in a round of funding led by One Ventures with participation from AM Ventures and existing investors.
Evove says it will use the funds to expand its manufacturing capacity, scale up its 3D-printed membrane process, and capitalize on its substantial pipeline of opportunities.
Researchers create graphene hydrogels for efficient water purification
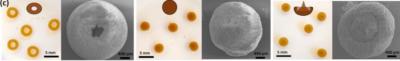
A team of researchers, led by Professor Aravind Vijayaraghavan based in the National Graphene Institute (NGI), have produced 3D particles made of graphene that come in various interesting shapes, using a variation of the vortex ring effect. These particles have also been shown to be exceptionally efficient in adsorbing contaminants from water, thereby purifying it.
Optical and SEM images of donut, spherical and jellyfish morphologies of GO-VR
The researchers have shown that the formation of these graphene particles is governed by a complex interplay between different forces such as viscosity, surface tension, inertia and electrostatics. Prof Vijayaraghavan said: “We have undertaken a systematic study to understand and explain the influence of various parameters and forces involved in the particle formation. Then, by tailoring this process, we have developed very efficient particles for adsorptive purification of contaminants from water”.
University of Manchester strikes graphene partnership with Khalifa University
The University of Manchester has entered a partnership with Abu Dhabi-based Khalifa University of Science and Technology, with the aim to deliver a funding boost to graphene innovation. Professor Dame Nancy Rothwell, President & Vice-Chancellor of The University of Manchester, and Professor Sir John O’Reilly, President of Khalifa University officially signed a contract between the two institutions during a VIP visit by a Manchester delegation to the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
This international partnership will further accelerate Manchester and Abu Dhabi’s research and innovation into graphene and other 2D materials. The Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC-2D), based in Khalifa University, is part of a strategic investment program supported by the Government of Abu Dhabi, UAE. This partnership will expedite the development of the RIC-2D at Khalifa University as well as help building capability in graphene and 2D materials in collaboration with Graphene@Manchester, a community that includes the academic–led National Graphene Institute (NGI) and the commercially-focused Graphene Engineering Innovation Centre (GEIC), a pioneering facility already backed by the Abu Dhabi-based renewable energy company Masdar.
Researchers create GO-based system for purifying river water
Researchers from India's Haldia Institute of Technology have created a gravity filter using graphene oxide (GO), meant for purifying river water. Using alternative water resources like river water can help address the rising shortage of freshwater resources worldwide. Therefore, the deployment of cost-effective water filtration technologies is imperative for the desalination of river water and purification of polluted water.
Filtration using a gravity filter is a highly popular method for water purification. A gravity filter is a type of pressure filter wherein water passes through the filtering component on the influent side at atmospheric pressure and the whole system is driven by the force of gravity instead of electricity. A major benefit of gravity filters is that they are free from moving components, therefore require less filter maintenance. Another significant advantage of using a gravity-based water filtration system is that the system does not need a power supply. The main drawback, on the other hand, is the low output of purified water. The limitations of filtering technology imply that no one filtration material can remove all pollutants present in water.
Levidian and United Utilities secure BEIS funding for biogas to hydrogen project
Levidian and United Utilities recently secured funding for the first phase of a biogas to hydrogen project.
The UK Government’s department for Business, Energy, and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) has awarded £212,000 (over USD$256,000) funding through the Net Zero Innovation Portfolio (NZIP) for the first phase of a project which will utilize biogas from wastewater treatment as a fully sustainable feedstock to produce hydrogen and graphene through the Levidian LOOP. United Utilities will lead the project.
Ultrathin covalent organic framework on graphene could be the key to better removal of pollutants
Researchers from the University of Vienna, South Korea's Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have reported an ultrathin covalent organic framework (COF) that was constructed homogeneously on the surface of a graphene template via a facile hydrothermal method.
The composite material of COF and graphene reportedly shows high and rapid adsorption capacity for organic pollutants.
Versarien launches graphene-based superparamagnetic material
Versarien has announced the launch of a new hybrid nanomaterial that has superparamagnetic properties, which can be used across a range of applications, like defense and healthcare. The new material combines graphene with both iron oxide and manganese oxide nanoparticles and its development was led by Versarien's 62% owned subsidiary, Gnanomat.
The superparamagnetic material combines graphene with both iron oxide and manganese oxide nanoparticles that provide the material with magnetic properties. In return, graphene provides electrical conductivity to these electrically insulating metal oxides. Magnetic nanocomposites can readily respond to external magnetic fields which allow them to be manipulated. Potential applications of the material include the treatment of wastewater whereby pollutants are adsorbed onto the graphene surface. The material could also lends be used in biomedical and biotechnology applications, or defense applications requiring the shielding of electromagnetic fields. Magnetic manipulation could allow the recovery and recycling of the graphene, something that could not be done with normal graphene compounds.
UAE launches a global graphene funding initiative
Khalifa University in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, have launched a new global graphene funding opportunity, aiming to support the development and applications of graphene (and other 2D materials) in the areas of composites (lightweighting), water and energy.
Khlaifa University established a new fund, called the RIC-2D Research and Innovation Fund, which will offer funding of up to $2 million per year for each project, for a maximum project duration of 3 years.
Researchers develop graphene-based foam composite for efficient water filtration
While graphene-based materials have potential as adsorbent materials, their performance can be hindered due to aggregation and a lack of control over their porosities and dimensions. The researchers in a recent study, from the University of Exeter, Kyushu University and the University of Oxford, have addressed this issue by developing a unique graphene material combined with a high porosity composite foam to combat aggregation.
Pharmaceuticals are among the most prominent emerging contaminants (ECs) in water systems. They may cause severe environmental consequences along with potential health problems. To successfully eradicate ECs from processed wastewater streams, effluent and drinking water purification facilities must adopt adequate tertiary treatment methods. Adsorption is regarded as a technology with great potential in water treatment as it is dependable and less expensive compared to reverse osmosis, oxidizing, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, ion exchange, etc.
Watercycle Technologies secures funding for its graphene-based membrane tech
Watercycle Technologies, a spin-out company from The University of Manchester, has secured initial funding for its technology that uses graphene-based membranes and systems to extract lithium and other minerals from brines and water solutions.
Led by Sebastian Leaper, a former PhD student from the Department of Materials at Manchester, Watercycle Technologies has taken Tier 2 membership of the Graphene Engineering Innovation Centre (GEIC), with lab space and access to advanced 2D materials facilities and expertise in prototyping.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page