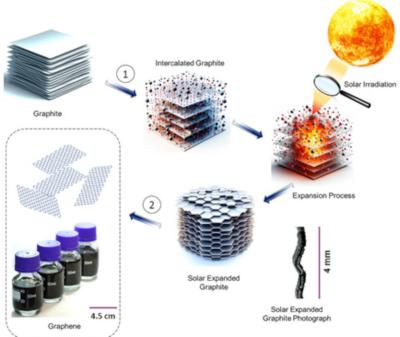
Researchers from Khalifa University of Science and Technology have demonstrated the production of few-layered graphene sheets with high lateral sizes (4–5 μm) through a state-of-the-art solar irradiation-driven liquid-phase exfoliation technique.
In this method, the sunlight is directly used on the intercalated graphite flakes for just 0.5 s to achieve the graphite expansion. Using focused sunlight makes this solar expansion technique sustainable with zero energy demand (0 J) - the total energy spent to produce 1 kg of graphene through this technique is only around 2.135 MJ.
The produced graphene sheets showed significant electrical conductivity (1586 S cm−1) and high in-plane thermal conductivity (196.3 W mK−1).
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding properties of solar graphene were evaluated in the X-band region, and reportedly showed a very high shielding effectiveness of about 71.5 dB at a thickness of ≈80 μm with an absolute EMI shielding effectiveness of about 11983.7 dB cm2 g−1.
Overall, this work provides a viable approach for the efficient, scalable production of graphene with reduced energy consumption and cost, contributing to the sustainable production of graphene.