Tata Steel develops a unique few-layer rGO film material
Tata Steel has developed a new product, a few-layer film of rGO along with its collaborators at CeNS, Bengaluru. The company is now starting to mass-produce the films and offer them to application developers.
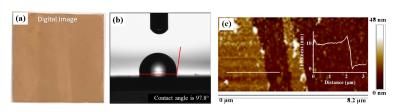
Figure 1: (a) Digital image of rGO/Cu foil (5 cm2). Contactact angle (b) and AFM height profile (c) on rGO/Cu
The rGO film is produced (using a modified CVD process) on copper. The film's average thickness is 5-10 nm and offers a corrosion rate of 0.02 mm/year (Tafel) and a water contact angle of ~ 97°.
These unique properties make the film suitable to protect the copper from corrosion, chemical attacks, and thermal oxidations. It also makes copper hydrophobic and can act as an antibacterial surface.