New graphene-based laser lift-off process enables ultrathin flexible displays
Researchers from Seoul National University of Science and Technology, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology and Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials recently reported a graphene-based laser lift-off technique that prevents damage while separating ultrathin OLED displays. This advancement could open the door towards ultra-thin, stretchable devices that fit comfortably against human skin, revolutionizing wearable device technology.
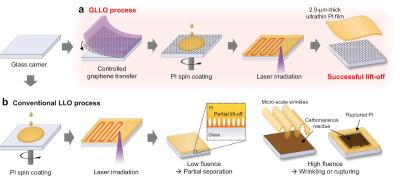
a) Graphene-enabled laser lift-off (GLLO) process. b) Conventional laser lift-off (LLO) process. Image from: Nature Communications
Polyimide (PI) films are widely used in these applications due to their excellent thermal stability and mechanical flexibility. They are crucial for emerging technologies like rollable displays, wearable sensors, and implantable photonic devices. However, when the thickness of these films is reduced below 5 μm, traditional laser lift-off (LLO) techniques often fail. Mechanical deformation, wrinkling, and leftover residues frequently compromise the quality and functionality of ultrathin devices, making the process inefficient and costly.