Graphene sensors: introduction and market status
What is a sensor?
A sensor is a device that detects events that occur in the physical environment (like light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure, and more), and responds with an output, usually an electrical, mechanical or optical signal. The household mercury thermometer is a simple example of a sensor - it detects temperature and reacts with a measurable expansion of liquid. Sensors are everywhere - they can be found in everyday applications like touch-sensitive elevator buttons and lamp dimmer surfaces that respond to touch, but there are also many kinds of sensors that go unnoticed by most - like sensors that are used in medicine, robotics, aerospace and more.
Traditional kinds of sensors include temperature, pressure (thermistors, thermocouples, and more), moisture, flow (electromagnetic, positional displacement and more), movement and proximity (capacitive, photoelectric, ultrasonic and more), though innumerable other versions exist. sensors are divided into two groups: active and passive sensors. Active sensors (such as photoconductive cells or light detection sensors) require a power supply while passive ones (radiometers, film photography) do not.
Where can sensors be found?
Sensors are used in numerous applications, and can roughly be arranged in groups by forms of use:
- Accelerometers: Micro Electro Mechanical technology based sensors, used mainly in mobile devices, medicine for patient monitoring (like pacemakers) and vehicular systems.
- Biosensors: electrochemical technology based sensors, used for food and water testing, medical devices, fitness tracker and wristbands (that measure, for example, blood oxygen levels and heart rate) and military uses (biological warfare and more).
- Image sensors: CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) based sensors, used in consumer electronics, biometrics, traffic and security surveillance and PC imaging.
- Motion Detectors: sensors which can be Infrared, Ultrasonic or Microwave/Radar technology. They are used in video games, security detection and light activation.
What is graphene?
Graphene is a two-dimensional material made of carbon atoms, often dubbed miracle material for its outstanding characteristics. It is 200 times stronger than steel at one atom thick, as well as the world's most conductive material. It is so dense that the smallest atom of Helium cannot pass through it, but is also lightweight and transparent. Since its isolation in 2004, researchers and companies alike are fervently studying graphene, which is set to revolutionize various markets and produce improved processes, better performing components and new products.
Graphene and sensors
Graphene and sensors are a natural combination, as graphene's large surface-to-volume ratio, unique optical properties, excellent electrical conductivity, high carrier mobility and density, high thermal conductivity and many other attributes can be greatly beneficial for sensor functions. The large surface area of graphene is able to enhance the surface loading of desired biomolecules, and excellent conductivity and small band gap can be beneficial for conducting electrons between biomolecules and the electrode surface.
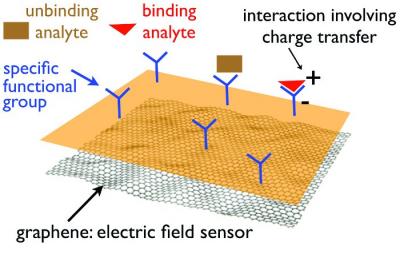
Graphene is thought to become especially widespread in biosensors and diagnostics. The large surface area of graphene can enhance the surface loading of desired biomolecules, and excellent conductivity and small band gap can be beneficial for conducting electrons between biomolecules and the electrode surface. Biosensors can be used, among other things, for the detection of a range of analytes like glucose, glutamate, cholesterol, hemoglobin and more. Graphene also has significant potential for enabling the development of electrochemical biosensors, based on direct electron transfer between the enzyme and the electrode surface.
Graphene will enable sensors that are smaller and lighter - providing endless design possibilities. They will also be more sensitive and able to detect smaller changes in matter, work more quickly and eventually even be less expensive than traditional sensors. Some graphene-based sensor designs contain a Field Effect Transistor (FET) with a graphene channel. Upon detection of the targeted analyte's binding, the current through the transistor changes, which sends a signal that can be analyzed to determine several variables.
Graphene-based nanoelectronic devices have also been researched for use in DNA sensors (for detecting nucleobases and nucleotides), Gas sensors (for detection of different gases), PH sensors, environmental contamination sensors, strain and pressure sensors, and more.
Commercial activities in the field of graphene sensors
In June 2015, A collaboration between Bosch, the Germany-based engineering giant, and scientists at the Max-Planck Institute for Solid State Research yielded a graphene-based magnetic sensor 100 times more sensitive than an equivalent device based on silicon.
In August 2014, the US based Graphene Frontier announced raising $1.6m to expand the development and manufacturing of their graphene functionalized GFET sensors. Their six sensors brand for highly sensitive chemical and biological sensors can be used to diagnose diseases with sensitivity and efficiency unparalleled by traditional sensors.
G-FET Six-Sensors
In September 2014, the German AMO developed a graphene-based photodetector in collaboration with Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs, which is said to be the world’s fastest photodetector.
In November 2013, Nokia's Cambridge research center developed a humidity sensor based on graphene oxide which is incredibly fast, thin, transparent, flexible and has great response and recovery times. Nokia also filed for a patent in August 2012 for a graphene-based photodetector that is transparent, thin and should ultimately be cheaper than traditional photodetectors.
Further reading
- Introduction to graphene
- Graphene company database
- How to invest in the graphene revolution
- The Graphene Handbook, our very own guide to the graphene market
- Graphene DNA Sequencing
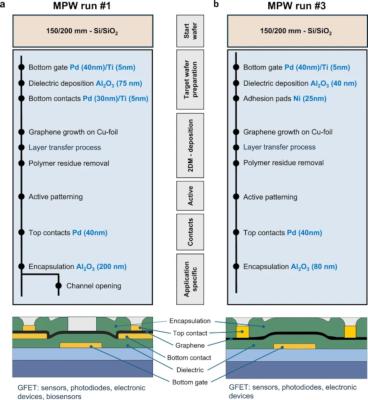
2D-EPL project reports results of two multi-project wafer runs
Researchers from AMO, Graphenea and RWTH Aachen University have, as part of the European experimental pilot line for electronic and optoelectronic devices based on graphene and related two-dimensional (2D) materials, namely the Experimental Pilot Line (2D-EPL) project, reported the results obtained during the first and third multi-project wafer (MPW) runs completed at the end of 2022 (MPW run 1) and 2023 (MPW run 3).
The Experimental Pilot Line (2D-EPL) project, that aims to advance the widespread commercialization of electronic devices based on graphene, published the new report that summarizes the results of two multi-project wafer (MPW) runs, utilizing electrical and spectroscopic characterization to demonstrate the high quality of production in the 2D-EPL. MPW run 1 was intended mainly for graphene-based sensors, in particular chemical and biosensors, while MPW run 3 focused on graphene electronics.
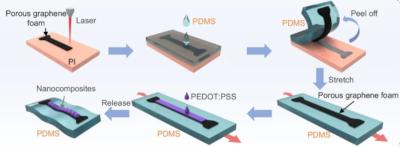
Laser-induced graphene-based sensor can separately measure temperature and physical strain
Researchers at Penn State and Hebei University of Technology recently developed stretchable thermoelectric porous graphene foam-based materials via facile laser scribing for self-powered decoupled strain and temperature sensing. The new sensor material enables precise and separate measurement of temperature and physical strain, a vital development for biosensors, for accurately tracking various health signals.
The team’s innovation is based on laser-induced graphene (LIG), created by using a laser to convert carbon-rich materials, such as plastic or wood, into graphene by heating their surfaces. This simple and scalable process is already used in a variety of applications, including gas sensors and electrochemical detectors. However, the scientists believe they have uncovered a new, critical property of LIG that makes it ideal for multi-signal sensing.
Novel graphene-based biosensing platform simultaneously detects vitamin C and SARS-CoV-2
Researchers from Penn State recently developed a portable and wireless device to simultaneously detect SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and vitamin C, a critical nutrient that helps bolster infection resistance, by integrating commercial transistors with printed laser-induced graphene.
By simultaneously detecting the virus and vitamin C levels, the test could help individuals and their health care providers decide on more effective treatment options, the researchers said. For example, someone with low vitamin C levels may benefit from a supplemental boost, while someone with normal or high vitamin C levels may need to consider other options.
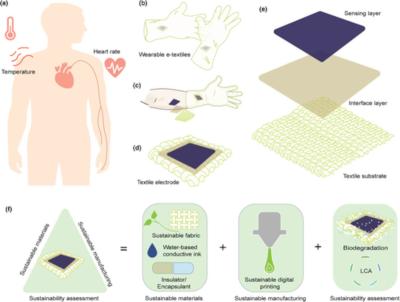
Graphene-based sustainable E-textiles for early detection of diseases
A research team, led by the University of Southampton and UWE Bristol, has developed graphene-based wearable electronic textiles (e-textiles) that are sustainable and biodegradable. In their new study, the team (which also involved the universities of Exeter, Cambridge, Leeds and Bath), describes and tests a new sustainable approach for fully inkjet-printed, eco-friendly e-textiles named 'Smart, Wearable, and Eco-friendly Electronic Textiles', or 'SWEET'.
a) Schematic of two important vital signs: skin surface temperature and heart rate of the human body. b) Schematic of wearable e-textiles as gloves. c) Schematic of the position of wearable textile electrode on human skin surface contact. d) Schematic of the textile electrode. e) Schematic of the textile electrodes' composition. f) Schematic of sustainable design approach for wearable e-textiles, including sustainable materials, sustainable manufacturing, and sustainability assessment. Image from: Energy and Environmental Materials
E-textiles are usually embedded with electrical components, such as sensors, batteries or lights. They might be used in fashion, for performance sportwear, or for medical purposes as garments that monitor people's vital signs. Such textiles need to be durable, safe to wear and comfortable, but also, in an industry which is increasingly concerned with clothing waste, they need to be easy on the environment when no longer required.
Versarien launches new graphene biosensor chip technology
Versarien has launched a new biosensor chip utilizing novel graphene barristor sensor platform technology. These graphene barristor devices, developed in South Korea by A Barristor Company (ABC), will utilize chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene, that is produced under a Versarien license. Versarien has signed a distribution agreement with ABC to distribute the products in the UK and Europe.
A barristor (triode device) is a new type of graphene‐based transistor with a Schottky barrier between graphene and silicon. The current modulation is amplified more than 10,000 times compared to graphene field‐effect transistors (GFET), enabling the barristor transistors to overcome many GFET limitations.
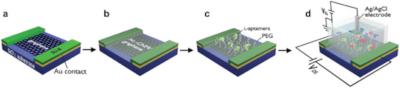
Graphene transistors could enable ultrasensitive detection of infections
Researchers from Friedrich Schiller University Jena, CNM Technologies, NOXXON Pharma, APTARION Biotech and Radboud University Medical Center have developed graphene field effect transistor (GFET) sensors based on van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures of single-layer graphene layered with a molecular ≈1 nm thick carbon nanomembrane (CNM).
1 / 1Schematic illustration of the fabrication steps of the l-AP/PEG-CNM GFET sensors. Credit: Advanced Materials
The CNM acts as an ultrathin molecular interposer between the graphene channel and the analyte and allows bio-functionalization without impairing the graphene properties including its charge carrier mobility.
Researchers demonstrate on-chip phonon-enhanced IR near-field detection of molecular vibrations
A team of Spain-based researchers has developed a highly sensitive detector for identifying molecules via their infrared vibrational “fingerprint”. The new detector converts incident infrared light into ultra-confined "nanolight" in the form of phonon polaritons within the detector´s active area. This mechanism serves two crucial purposes: it improves the detector's overall sensitivity and enhances the vibrational fingerprint of nanometer-thin molecular layer placed on top of the detector, allowing this molecular fingerprint to be more easily detected and analyzed.
The compact design and room-temperature operation of the device hold promise for developing ultra-compact platforms for molecular and gas sensing applications.
Zentek and Triera Biosciences receive USD$791,000 from Government of Canada to test multivalent aptamer technology
Zentek has announced that its wholly-owned subsidiary Triera Biosciences has received a CAD$1.1 million (around USD$791,000) Government of Canada contract to test its multivalent aptamer technology for the rapid drug discovery of therapeutics or prophylactics of highly pathogenic avian influenza (“HPAI”) A(H5N1).
Triera was awarded a these funds through Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada's (“ISED”) Innovative Solutions Canada (“ISC”) program: Health Advanced And Emerging Medical Technologies. Triera’s multivalent aptamer technology was selected for its potential to be used as a rapid drug development platform.
Researchers develop a new process for laser-induced graphene smart textile that could improve space gear
Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials and Seoul National University of Science and Technology (SEOULTECH) have shown that laser-induced graphene (LIG), patterned with femtosecond laser pulses, can serve as a versatile material for temperature/strain sensing, stray light absorption, and heat management for smart spacesuits and telescopes.
Direct laser writing of laser-induced graphene (LIG). Image from: Advanced Functional Materials
The team has developed a manufacturing technique that addresses the challenges posed by the harsh conditions that space equipment must function in. The scientists' new process uses precisely controlled laser pulses to transform a Kevlar's surface into a porous graphene structure, effectively converting ordinary Kevlar fabric into a multifunctional material.
Novel graphene-based sensor system rapidly detects toxic gas
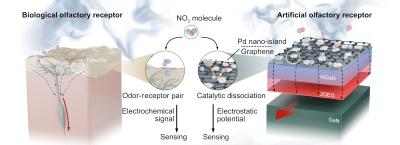
Researchers at the University of Virginia, Ajou University and Soongsil University have developed an AI-powered system that mimics the human sense of smell to detect and track toxic gases in real time. Using advanced artificial neural networks combined with a network of sensors, the system quickly identifies the source of harmful gases like nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) that poses severe respiratory health risks.
Schematic of biological and artificial olfactory receptor. Biological receptors interact with odor molecules through specific binding, whereas artificial receptors use catalytic dissociation by Pd nano-islands for selective gas molecule adsorption on graphene surfaces. Image credit: Science Advances
The artificial olfactory receptor features nano-islands of metal-based catalysts that cover a graphene surface on the heterostructure of an AlGaN/GaN two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) channel. Catalytically dissociated NO2 molecules bind to graphene, thereby modulating the conductivity of the 2DEG channel and allowing the system to detect gas leaks with extreme sensitivity.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page